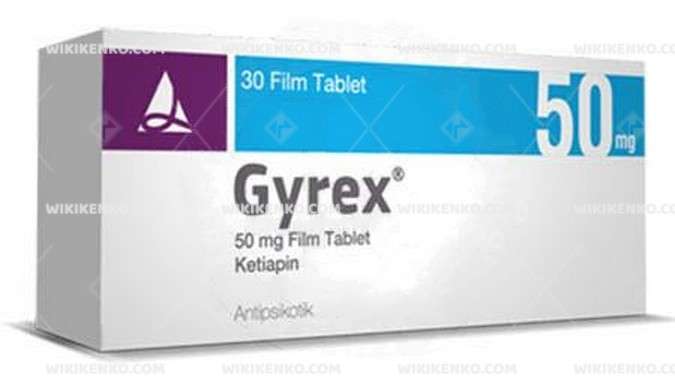
Gyrex Film Coated Tablet 50 Mg
Gyrex is a film-coated tablet that contains 50 mg of the active ingredient ketiapin. It is an antipsychotic medication used in the treatment of psychiatric disorders.
| Dosage form | |
|---|---|
| Pack size | |
| Potency | 50 Mg |
| Manufacturer | |
| Origin | |
| Generic Name (Ingredient) | Each Film Tablet Contains 50 Mg Of Quetiapine Base (57.565 Mg As Quetiapine Fumarate). |
Assuming your emergency circumstances for this product, visit Urgent Quotation page. Besides, for any pharmaceutical questions, please ask us in the comments section.
Description
Ingredients
Each film-coated tablet contains 50 mg of ketiapin, which is equivalent to 57.565 mg of ketiapin fumarate. The tablet also contains several excipients, including polivinil pirolidon, calcium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, sodium starch glycolate, lactose monohydrate (sourced from cattle), magnesium stearate, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, titanium dioxide, talc, and polyethylene glycol.
Indications
Gyrex is effective in treating the following conditions:
- Major Depressive Episodes Associated with Bipolar Disorder: This condition includes symptoms such as sadness, pessimism, guilt, loss of energy, decreased appetite, and insomnia.
- Moderate to Severe Manic Episodes in Bipolar Disorder: These episodes may manifest as excessive joy, excitement, happiness, curiosity, hyperactivity, aggressive behaviors, and impaired decision-making.
- Prevention of Recurrence of Manic and Depressive Episodes in Bipolar Disorder: For patients who have previously responded to ketiapin treatment.
- Schizophrenia: Symptoms may include hallucinations, delusions, suspicion, anxiety, confusion, guilt, tension, and boredom.
Precautions
Gyrex should not be used by elderly patients with dementia, a condition characterized by a loss of brain function affecting memory and thinking. Its use in such patients can increase the risk of stroke and, in some cases, death.
Packaging
Gyrex is conveniently packaged in blister packs containing 30, 60, and 90 tablets. These tablets are white, round, and convex on one side, bearing the logo “Q50.”
Please note that the information provided here is for reference and does not replace the recommendations or advice of your physician or pharmacist. Always consult your healthcare professional if you have additional questions.
Side Effects
The side effects of Gyrex Film Coated Tablet 50 Mg can be classified based on their frequency:
Very Common Side Effects
These side effects can occur in at least 1 in 10 patients:
- Dizziness (may lead to fainting)
- Dry mouth
- Sleepiness (may lead to fainting)
- Weight gain
- Abnormal muscle movements, including difficulty initiating movements, tremors, discomfort, or painless muscle stiffness.
Common Side Effects
These side effects can occur in less than 1 in 10 patients but more than 1 in 100 patients:
- Increased heart rate (tachycardia)
- Nasal congestion
- Constipation and indigestion
- Feelings of weakness and fatigue
- Swelling in the arms or legs
- Drop in blood pressure upon standing (orthostatic hypotension), which may lead to feelings of dizziness or fainting and an increased risk of falls
- Increased blood sugar levels
- Blurred vision
- Abnormal dreams and nightmares
- Increased appetite
- Irritability
- Difficulty in speech and pronunciation.
Please note that this list does not encompass all possible side effects. If you experience any other side effects not mentioned here, discontinue Gyrex and consult your doctor immediately. It’s essential to remember that while many people may experience no or minor side effects, all medicines can potentially cause adverse reactions.
How to Take Gyrex
Gyrex should be taken orally as directed by your healthcare provider. The specific dosage and frequency of use depend on the condition being treated and your individual response to the medication. It’s crucial to adhere to your doctor’s instructions carefully, avoiding doses higher or lower than recommended. If you have any questions about how to take Gyrex, consult your healthcare provider or pharmacist, who can provide guidance tailored to your health history and current situation.
Pregnancy or Breastfeeding
Note: Information regarding the safety of Gyrex during pregnancy or breastfeeding is not available in the provided text. For guidance in these situations, it is essential to consult with your healthcare provider for the most accurate and up-to-date information.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Gyrex Film Coated Tablet 50 Mg is a medication used in the treatment of various psychiatric conditions, including bipolar disorder, manic episodes, and schizophrenia. While effective, it is essential to take precautions, be aware of potential side effects, and follow your healthcare provider’s guidance for safe and effective use. Always consult with your healthcare professional for personalized advice and information, especially during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
At a glance
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Medication Type | Antipsychotic Medication |
| Active Ingredient | Ketiapin |
| Equivalent Dose | 50 mg of Ketiapin Fumarate |
| Indications | Bipolar Disorder, Manic Episodes, Bipolar Depression, Schizophrenia |
| Precautions | Not Suitable for Elderly Patients with Dementia |
| Packaging | Available in Blister Packs of 30, 60, and 90 Tablets |
| Common Side Effects | Dizziness, Dry Mouth, Sleepiness, Weight Gain, Abnormal Muscle Movements, Increased Heart Rate, Nasal Congestion, Constipation, Weakness, Swelling, Orthostatic Hypotension, Increased Blood Sugar, Blurred Vision, Abnormal Dreams, Hunger, Irritability, Speech Difficulty |
| How to Take | Orally, Follow Doctor’s Instructions |
Use the form below to report an error
Please answer the questions as thoroughly and accurately as possible. Your answers will help us better understand what kind of mistakes happen, why and where they happen, and in the end the purpose is to build a better archive to guide researchers and professionals around the world.
The information on this page is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. always seek the advice for your physician or another qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Always remember to
- Ask your own doctor for medical advice.
- Names, brands, and dosage may differ between countries.
- When not feeling well, or experiencing side effects always contact your own doctor.
Cyberchondria
The truth is that when we’re sick, or worried about getting sick, the internet won’t help.
According to Wikipedia, cyberchondria is a mental disorder consisting in the desire to independently make a diagnosis based on the symptoms of diseases described on Internet sites.
Why you can't look for symptoms on the Internet
If diagnoses could be made simply from a textbook or an article on a website, we would all be doctors and treat ourselves. Nothing can replace the experience and knowledge of specially trained people. As in any field, in medicine there are unscrupulous specialists, differences of opinion, inaccurate diagnoses and incorrect test results.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.